Onduo Data Presented at American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) 80th Scientific Sessions Highlights Meaningfully Lowered Hemoglobin A1C in People with T2D, with Significantly Greater Reductions in Participants Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Onduo Data Presented at American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) 80th Scientific Sessions Highlights Meaningfully Lowered Hemoglobin A1C in People with T2D, with Significantly Greater Reductions in Participants Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Additional real-world evidence presented at ADA and published in Clinical Diabetes shows participation in Onduo virtual care program reduces diabetes-related distress in participants with elevated baseline distress
Onduo to host webinar on Monday, July 6th at 2 pm ET to discuss future of virtual care and CGMs
BOSTON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--This week Onduo presented research results at the American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) 80th Scientific Sessions: A Virtual Experience demonstrating continued and meaningful improvement in outcomes among participants living with type 2 diabetes (T2D). These data separately show that:
- Participants in the Onduo program experienced significant reductions in HbA1C, the standard measurement of glycemic control. The use of CGM in the highest risk group (baseline HbA1C over 9.0%) resulted in the greatest average HbA1C drop (-3.3%).1
- Diabetes-related distress, which is associated with poor health outcomes in T2D, improved significantly among participants with elevated baseline distress. Improvements in regimen-related and emotional distress were most notable.2
- In a prospective study, Onduo participants saw a significant 10.2% increase in time in target glucose range (time in range), which is equivalent to an additional 2.4 hours per day.3
These new data add to the growing body of evidence supporting Onduo’s comprehensive virtual care program. In 2019, Onduo published a real-world study5 reporting clinically significant improvement in HbA1C in 740 participants, with an average of reduction of 2.3% for those with baseline HbA1C > 9.0%.
More information on the data presented at ADA is below.
Oral Presentation #70-OR: Change in A1C With and Without Intermittent Use of CGM in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Participating in the Onduo Virtual Diabetes Clinic
In a real-world analysis (n=612),1 participation in Onduo for six months was associated with significant improvement in HbA1C - both with and without use of CGM. An elevated HbA1C reflects high blood sugar levels and is a risk factor for diabetes-related complications; according to the ADA, most adults with diabetes should target an HbA1C level below 7.0%.
- Among those who did not use CGM (n=399), HbA1C decreased by 0.4% from a baseline of 7.7% (p<0.001).
- Among those who used CGM (n=213), HbA1C decreased by 0.9% from a baseline of 7.9% (p<0.001).
- Among those with an HbA1C > 9.0% at baseline, the group who used CGM saw a nearly two-fold greater decrease in HbA1C compared to the group who did not use CGM, 3.3% vs. 1.7%, respectively (p<0.001).
These observations suggest that Onduo’s care model and CGM work hand-in-hand to improve outcomes.
“We need to see a change in the way we empower people living with type 2 diabetes to manage their care,” said Dr. Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, Chief Scientific and Medical Officer, American Diabetes Association and a co-author in the abstract. “There is a real benefit in integrating a connected device like a CGM within a personalized, remote support and virtual care model like Onduo’s. It encourages and facilitates shared decision-making and improved self-management, both of which are foundational to diabetes care.”
Oral Presentation 12-OR: Participation in a Virtual Diabetes Clinic and Reduced Diabetes-related Distress in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
In another real-world analysis (n=228),2 participation in Onduo was associated with significantly reduced diabetes-related distress. The Diabetes Distress Scale (DDS) evaluates stress on a 6-point scale ranging from “not a problem” to “a very serious problem”.
- Among participants with clinically-relevant diabetes-related distress, mean overall DDS score fell significantly from 3.0 to 2.5 (p<0.001) after an average of six months in Onduo’s program.
- Improvements on the regimen-related and emotional distress subscales were most notable, with scores falling by 0.9 and 0.4 points (both p<0.001), respectively.
These results were also recently published in Clinical Diabetes (a journal of the ADA).4 This study suggests that Onduo’s relationship-based care approach, which focuses on whole person health and places value on both physical and emotional health, helps people to more confidently manage their diabetes.
“Diabetes distress is a major obstacle to successful self-management and is associated with problematic adherence and poor health outcomes,” said William H. Polonsky, PhD, CDCES, President of the Behavioral Diabetes Institute, Associate Professor of Psychology at the University of San Diego, CA, and lead author of the Clinical Diabetes article. “It is encouraging that elevated levels of distress dropped markedly among participants in Onduo’s program, which may help to make way for improved clinical outcomes.”
Poster Presentation #77-LB: Improved A1C and TIR in Adults With T2D Participating in a CGM driven Virtual Diabetes Clinic
Onduo presented results from a prospective study3 in 55 adults with type 2 diabetes, recruited from two primary care centers, who participated in Onduo’s virtual clinic for four months. Notably, this is the first report of CGM-based glycemic metrics in a telehealth program for type 2 diabetes that provides CGM for participants.
- Participants saw an average decrease in HbA1C of 1.6%, and those with an average baseline HbA1C greater than 9% saw a decrease in HbA1C by 2.4% (both p<0.001).
- Participants saw a 10.2% increase in time in target blood glucose range (p=0.002), which is equivalent to an additional 2.4 hours per day.
- Other common risk factors for people with diabetes—weight, blood pressure, and blood lipid levels—also significantly improved among participants in the study.
“Together, these data demonstrate how combining advanced technology with a personalized, relationship-based virtual care model can positively impact both health outcomes and quality of life,” said Dr. Ronald Dixon, MD, Onduo’s Head of Clinical Affairs. “The common thread through these findings is that CGM augments the effects of our program. Moving forward, we are exploring ways to more broadly and creatively integrate CGM into our program to promote better health for the most people possible.”
Upcoming Webinar
Onduo’s Ronald Dixon, MD will also host a webinar on Monday, July 6th at 2 pm ET to reflect on the research presented at the ADA’s 80th Scientific Sessions and discuss exciting frontiers in technology-enabled management of type 2 diabetes. Webinar participants include:
- Richard Bergenstal, MD - Executive Director, International Diabetes Center at Park Nicollet
- David Price, MD - VP of Medical Affairs, Dexcom
- And more (to be confirmed)
To join the discussion, go here to register.
About Onduo
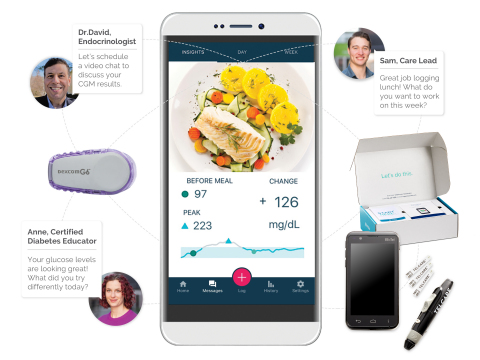
Onduo’s virtual care model matches participants with a personalized behavior-change program supported by health and lifestyle coaches, connected tools and devices, and clinical support from certified diabetes care and education specialists (CDCES) and board-certified endocrinologists. Key features include live video consultations with endocrinologists for medication management and prescription of CGMs, which Onduo ships directly to participants with support for placement. Launched as a joint venture in 2016, Onduo is working closely with Verily (an Alphabet company) to build a team of talented people committed to creating a next generation platform that will help people live well, while managing their health holistically. Onduo headquarters are based out of Newton, MA.
References
1Layne JE, Zisser H, Bergenstal RM, Gabbay RA, Barleen NA, Miller DP, Dixon RF. Change in A1c With and Without Intermittent Use of CGM In Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Participating in the Onduo Virtual Diabetes Clinic. Diabetes 2020 Jun; 69 (Supplement 1). doi.org/10.2337/db20-70-OR
2Polonsky WH, Layne JE, Parkin CG, Kusiak CM, Barleen NA, Miller DP, Zisser H, Dixon RF. Participation in a Virtual Diabetes Clinic and Reduced Diabetes-Related Distress in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2020 Jun; 69 (Supplement 1). doi.org/10.2337/db20-12-OR
3Majithia AR, Kusiak CM, Armento Lee A, Colangelo FR, Romanelli R, Robertson S, Miller DP, Erani DM, Dixon RF, Zisser H. Improved A1c and TIR in Adults With T2D Participating in a CGM Driven Virtual Diabetes Clinic. DIabetes 2020 Jun; 69 (Supplement 1). doi.org/10.2337/db20-77-LB
4Polonsky, WH, Layne JE, Parkin CG, Kusiak CM, Barleen NA, Miller DP, Zisser H, Dixon RF. The Impact of Participation in a Virtual Diabetes Clinic on Diabetes-Related Distress in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Clinical Diabetes, ePub June 12, 2020.
5Dixon RF, Zisser H, Layne JE, Barleen NA, Miller DP, Moloney DP, Majithia AR, Gabbay RA, Riff J. A Smartphone-Based Type 2 Diabetes Clinic Using Video Endocrinology Consultations and CGM. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019. ePub November 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296819888662
Contacts
Lori Scanlon
774-217-1330
press@onduo.com