LEMONT, Ill.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Flexible, wearable electronics are making their way into everyday use, and their full potential is still to be realized. Soon, this technology could be used for precision medical sensors attached to the skin, designed to perform health-monitoring and diagnosis. It would be like having a high-tech medical center at your instant beck and call.
Such a skin-like device is being developed in a project between the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME).
Worn routinely, future wearable electronics could potentially detect possible emerging health problems even before obvious symptoms appear. The device could also do a personalized analysis of the tracked health data while minimizing the need for its wireless transmission.
Such a device would need to collect and process a vast amount of data, well above what even the best smartwatches can do today. And it would have to do this data crunching with very low power consumption in a very tiny space.
To address that need, the team called upon neuromorphic computing. This artificial intelligence (AI) technology mimics operation of the brain by training on past data sets and learning from experience. Its advantages include compatibility with stretchable material, lower energy consumption and faster speed than other types of AI.
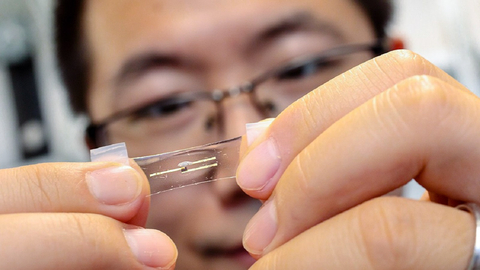
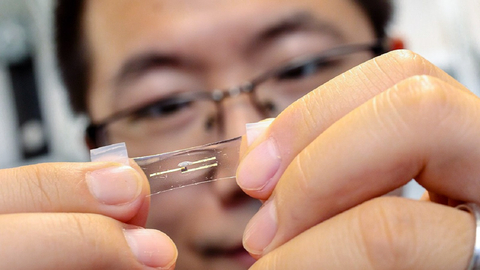
The other major challenge the team faced was integrating the electronics into a skin-like stretchable material. The key material in any electronic device is a semiconductor. In current rigid electronics used in cell phones and computers, this is normally a solid silicon chip. Stretchable electronics require that the semiconductor be a highly flexible material that is still able to conduct electricity.
The team’s skin-like neuromorphic “chip” consists of a thin film of a plastic semiconductor combined with stretchable gold nanowire electrodes. Even when stretched to twice its normal size, their device functioned as planned without formation of any cracks.
As one test, the team built an AI device and trained it to distinguish healthy electrocardiogram (ECG) signals from four different signals indicating health problems. After training, the device was more than 95% effective at correctly identifying the ECG signals.
Exposure to an intense X-ray beam revealed how the molecules that make up the skin-like device material re-organize upon doubling in length. These results provided molecular-level information to better understand the material properties.