AUSTIN, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--DiFusion Inc, unveiled groundbreaking Osteoimmunology data at the North American Spine Society 2020 Annual Meeting demonstrating the superiority of the new biomaterial ZFUZE over Nano-Surfaced Titanium and conventional PEEK materials. ZFUZE is the first biomaterial specifically engineered to interact with the human immune system such that the human immune system does not attack it as a foreign body. These foreign body responses lead to long-term chronic inflammation and a multitude of patient complications.
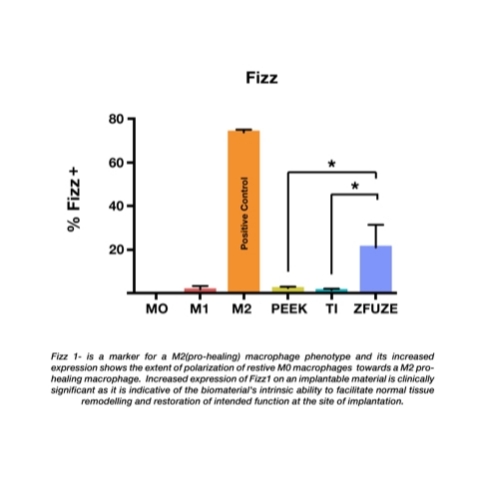
The Osteoimmunology research was conducted at the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh by Stephen Badylak, MD, DVM, PhD. A series of N-powered cellular assays were studied which compared Macrophage Polarization, Osteoblast Growth, and Bone Morphogenic Protein Upregulation. ZFUZE outperformed Nano-surfaced Titanium and conventional PEEK on a statistically significant basis across all three studies. The testing was conducted in triplicate and the results are being submitted to major peer reviewed journals for publication. The North American Spine Society presentation can be viewed here.
“The results from Dr. Badylak’s study support a growing body of clinical evidence that supplements our previous animal testing and explains the large statistically significant reductions in Interleukin 1-beta which we observed in our ZFUZE sheep study. In tandem, these results are groundbreaking and put DiFusion at the forefront of biomaterial research,” said Derrick Johns CEO of DiFusion. “We also are just getting early CT scans in from our first human spinal fusion surgeries and are seeing phenomenal results at the 5, 6 and 7-month timepoint with visible boney ongrowth and ingrowth in early patients.”
Titanium was first borrowed from the aerospace industry for dental implants, then moved to the hip and knee replacement market and most recently into 3D printed spinal implants. Titanium has been the mainstay orthopedic material for decades due to its strength and anti-corrosive properties. However, wear debris from Titanium also has a long-documented history of causing problems in dental implants and in hip and knee replacements. The FDA recently held a hearing on “Metal Wear Debris” and is considering new labeling requirements for manufacturers. See additional details at FDA Hearing: Metal Poisoning.
“There has been a substantial increase in the promotion of surface-enhanced Titanium medical devices over the past few years. It seems appropriate and timely to recognize the relevance and critical role for patient’s immune response in determining clinical outcome. It is now irrefutable that the osteo-immunologic response to devices and new biomaterials such as ZFUZE, as opposed to simply mechanical and surface properties of Titanium, is paramount to long term efficacy and patient healing,” Stephen Badylak, DVM, MD, PhD., Deputy Director of the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
DiFusion Inc, is biomaterial research and development company offering specialty immunomodulating polymers for the Orthopedic Spine, Total Joint, Sports Medicine, and Neurosurgery market. DiFusion received FDA clearance for ZFUZE Spinal Fusion devices in November of 2019 and has now been used on more than 100 surgeries, despite the suspension of elective surgeries due to COVID-19 in some parts of the country.
References:
Osteoimmunology of Biomaterials: Stephen Badylak, DVM, MD, PhD., Joe Bartolucci, MS, Arthi Shridhar, PhD., Sriram Sankar, MS – North American Spine Society 2020
Titanium: a review on exposure, release, penetration, allergy, epidemiology, and clinical reactivity: Simon W. Fage1, Joris Muris2, Stig S. Jakobsen3 and Jacob P. Thyssen4
The Effects of Biomaterial Implant Wear Debris on Osteoblast: Li Zhang, Kristian Welle, Christof Burger, Frank Shildberg. Clinic for Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery, University Hospital Bonn, Bonn, Germany
Severe metallosis-related osteolysis as a cause of failure after total knee replacement: Khaled Hamed Salem, Norbert Lindner, Markus Tingart, Alyaa Diaa Elmoghazy