HSINCHU, Taiwan--(BUSINESS WIRE)--On February 14th the melodious strains of the fourth movement of Mahler's Fifth Symphony were heard inside the building of Tsing Hua Open pool Reactor (THOR) at National Tsing Hua University (NTHU) - for this is the favorite piece of music of a European woman who was here to undergo Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) for a malignant brain tumor. This was her second course of treatment. The size of malignant glioma deep in her brainstem was reduced from 3.51 cm to 1.06 cm after the first treatment.
In cooperation with the Taipei Veterans General Hospital (TVGH), NTHU has converted THOR for use in BNCT. To date, the treatment has provided a new lease on life to over 130 cancer patients from around the world.
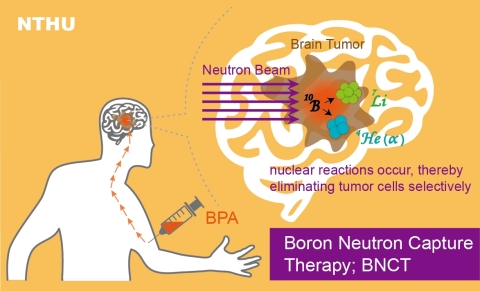
According to Professor Chou Fong-in, BNCT is a target radiation therapy in which the patient is first injected with a boron-containing drug; once the drug has accumulated in the tumor, the neutron beam is used to irradiate the tumor for delivering curative doses specifically to tumors, while sparing normal tissue.
As explained by TVGH oncologist Chen Yi-wei, boron-10 drug contains the structure like essential amino acids, and cancer cells need lots of nutrients to support their abnormal proliferation. Thus cancerous cells absorb almost all the boron-10 before the normal cells have a chance to. The boron acts as a kind of explosive charge, and once the cancerous cells have got their fill of it, the neutron beam is used to “detonate” the charge, killing off the cancer cells.
The husband of the patient is a physician. He said that his wife used to be an avid tennis player, but four years ago she unexpectedly saw two balls flying towards her at the same time, a classic symptom of diplopia. A computerized tomography (CT) scan, however, later revealed a lesion of glioma in her brain, located deep inside her brainstem. After undergoing two craniotomies with gamma knife radiotherapy, the glioma relapsed and had turned malignant. On the advice of an expert of Radiation Oncology, they inquired about the treatment being offered at the TVGH.
According to Dr. Chen, the key requirements for BNCT are a boron-containing drug suitable for absorption by cancer cells, and a stable neutron source with appropriate energy spectrum. NTHU’s research reactor has been retrofitted to provide the neutron source. It is even better than the accelerator driven neutron source developed in Japan for use in hospitals.
NTHU and the Taoyuan City Government are planning to jointly develop a medical complex as part of the Taoyuan Aerotropolis to be built near the Taoyuan Airport. The BNCT will play a major role at the new facility, and will be used to treat both Taiwanese and overseas patients.