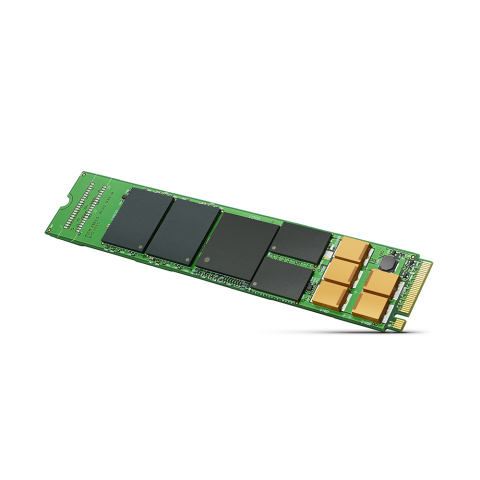
CUPERTINO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Seagate Technology plc (NASDAQ: STX), today unveiled a first-of-its kind, high-capacity drive that can help data centers more easily accommodate exponential data growth, while still maintaining high levels of computing power and performance. The two terabyte (TB) version of its Nytro® XM1440 M.2 non-volatile memory express (NVMe) Solid State Drive (SSD) is the highest-capacity, enterprise-class M.2 NVMe SSD available today, making it well suited for demanding enterprise applications that require fast data access, capacity and processing.
As the latest addition to the Seagate Nytro SSD product line, the 2TB Nytro XM1440 M.2 NVMe SSD is designed to accelerate enterprise data access, with twice the density of prior M.2 NVMe environments. Optimized for read-intensive and mixed workloads, its high capacity and small form factor are ideal for today’s cloud and enterprise data center environments, where speed and processing power in a small footprint are increasingly important. The drive can help meet the needs of demanding enterprise applications including online transaction processing, high-performance computing and big data analytics. It also helps manage storage growth with deduplication and compression, allowing data centers to easily create more virtual machines instantly without having to add additional servers — enabling today’s data centers to more easily manage their ever-expanding storage growth.
“Data and time are money, and nowhere is this more apparent than in today’s enterprises, which are grappling with how to accommodate ever-increasing amounts of data without losing the ability to quickly access and process it to continue deriving value,” said Brett Pemble, Seagate’s general manager and vice president of SSD products. “This latest version of the Nytro XM1440 M.2 NVMe SSD is the first of its kind and pushes the boundaries for enterprises, so they don’t have to sacrifice speed for access and availability. They can continue to scale operations in an efficient manner and still get the most value from their data, but without the extra overhead.”
With active power consumption of 7 watts — nearly half the power consumption of similar performing drives available today — the 2TB Nytro XM1440 M.2 NVMe SSD can reach performance levels as high as 30,000 input/output operations per second (IOPS) per watt, enabling high levels of computing in the smallest power envelope. And, the drive’s flexible form factor means enterprises can easily bring PCIe NVMe performance to their data centers without having to overhaul their entire infrastructure.
The 2TB Nytro XM1440 M.2 NVMe SSD has end-to-end data protection, including low-density parity-check error correction and RAISE™ technology, which delivers RAID-like data protection and recovery from potentially catastrophic flash memory failures. The drive also comes with a power loss data protection circuit to help prevent data loss in the event of a power interruption.
The 2TB Nytro XM1440 M.2 NVMe SSD will be available through channel partners in November 2016.
For datacenters not yet prepared to utilize the new M.2 interface, this same solution is also available as the new Nytro XP7102 PCIe NVMe Add-in Card, available through channel partners now.
About Seagate
Seagate creates space for the human experience by innovating how data is stored, shared and used. Learn more at www.seagate.com. Follow Seagate on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Spiceworks, YouTube and subscribe to our blog.
©2016 Seagate Technology LLC. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. Seagate, Seagate Technology, Nytro, RAISE and the Seagate logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC or its affiliates in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Seagate reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications. When referring to drive capacity, one terabyte, or TB, equals one thousand billion bytes. Your computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement and report a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions and will not be available for data storage.